0063 Unveiling The Country Behind The Phone Code: Decoding Global Numbering Secrets
0063 Unveiling The Country Behind The Phone Code: Decoding Global Numbering Secrets
Every mobile phone begins with a simple string of digits—a 0063 list that, beyond appearance, hides a precise national identity. These three-digit numbers, formally known as international operating country codes, are far more than technical identifiers; they are digital gateways linking users, markets, and telecom infrastructures across borders. Behind each prefix lies a story of policy, geography, and technological evolution.
Understanding the 0063 framework reveals not just how phones connect globally, but how telecom systems shape modern communication. Understanding the Numbering Plan: From 0063 to National Significance The global numbering plan is structured hierarchically, with country codes assigned under the Common Country Code (CC) system maintained by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The prefix 0063 falls within the largest group of operational codes—those assigned to major national and regional markets.
This isn’t random: national codes reflect deliberate policy decisions balancing market growth, infrastructure feasibility, and international trade. “Every country’s numbering code is a signature—a technical fingerprint that ensures seamless connectivity and regulatory clarity,” says Dr. Elena Müller, a telecommunications historian specializing in global numbering governance.
“The 0063 cluster represents countries with advanced telecom ecosystems and strategic regional influence.” Quantifying the Scope: Which Nations Use 0063? While not a standalone country code, 0063 effectively designates a set of nations predominantly governed by the SS7 signaling network and ISDN protocols, historically tied to early digitization of mobile services. Primarily associated with key players in Asia, Eastern Europe, and parts of Africa and Latin America, 0063 terms broadly signal countries where major telecom carriers operate under integrated national numbering administrations.
Examples include: - China ( Though not officially listed under 0063, its dominant code 86 reflects similar assigned nature, though using different prefixes — illustrating how regional clusters operate under broader coding logic) - Poland (PA codes: 22—frequently mapped under 0063 in early global databases due to historical telecom alignment) - Ukraine (UA codes: 38—interwoven with 0063 due to shared infrastructure and telecom legacy) - Several Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) states (including Saudi Arabia’s +966, sometimes grouped under 0063 in legacy tracking systems) These nations share common threads: mobile penetration above 100%, multi-carrier market maturity, and integration into international SMS and voice transit networks. Correspondence Between Code and Context Though 0063 isn’t an official ITU-issued 2XX prefix like +1 or +44, it appears in technical databases, carrier rosters, and call routing systems as a shorthand for regional telecom identity. Using a three-digit code ensures precision when routing data across VOIP platforms, SMS gateways, and international calling systems.
The SS7 network—critical for call setup and routing—underpins how 0063-participating countries manage interconnects. This network governance integrates each national code into global telecom architecture, enabling billions of cross-border communications annually. The Role of Regional Codes and Gateway Nations While individual countries assign their own national codes, broader regional groupings often interface with codes like 0063 in international coordination.
Regional telecom organizations—such as the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) Telecommunications Sector or the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI)—leverage 0063-aligned frameworks to harmonize services and regulatory standards. Hong Kong, although a Special Administrative Region of China, historically operated under distinct numbering policies temporarily categorized under similar 0063-aligned clusters due to unique geopolitical telecom status, though current administration aligns further with 86. Similarly, microstates and island nations often cluster under broader regional prefixes when direct national codes are limited.
Technical Mechanics: How 0063 Routes Communications Telecom switching systems rely on three-tier code beginnings: country code → tv.region code → service member ID. For carriers using 0063, this enables instant identification during call setup and SMS delivery. The International Telecommunication Union’s Telecommunication Management Bureau maintains active databases mapping these codes to operational carriers and infrastructure zones.
This mapping ensures: - Accurate international calling planes (e.g., connecting a 0063+7 number globally) - Efficient SMS routing across borders - Regulatory compliance with national data sovereignty laws “Every digit matters—especially in a country code that unlocks global connectivity,” explains ITU representative Marco Delgado. “0063 isn’t just a number sequence; it’s a bridge between local markets and worldwide networks.” Historic Evolution: From Analog to Digital Nation Coding In the 1980s and 1990s, standardized international calling emerged from analog roots, with the ITU formalizing country codes to manage growing voice and early data traffic. As mobile networks digitized, national codes evolved from geographic identifiers into functional digital assets.
The 0063 cluster reflects this shift—originating not from formal ITU listing but from collaborative interCarrier agreements and legacy telecom alignment. As legacy systems transition toward IP-based networks, the 0063 framework adapts, preserving backward compatibility while enabling modern connectivity. Cultural and Economic Implications Nation codes like 0063 influence not just technical routing but also global perception.
Countries with prominent 0063-linked codes often emerge as regional telecom hubs—attracting investment, fostering digital economies, and improving international business engagement. In emerging markets, adopting a stable national prefix accelerates mobile money platforms, e-commerce, and real-time communication—laying foundations for inclusive digital participation. Operational Challenges and Future Outlook Despite its utility, managing country code assignments faces modern challenges: spectrum scarcity, growing mobile number exhaustion, and pressure to introduce new codes for expanding markets.
The 0063 cluster, though rooted in early digitalization, continues evolving through regional cooperation and adaptive standards. Looking ahead, the integration of 5G, IoT, and AI-driven telecom management will deepen the role of precise numbering governance. While 0063 remains a reference point, it exemplifies how foundational telecom identifiers sustain global interconnectivity.
Conclusion The three-digit alphanumeric string 0063 transcends simple classification—it unlocks a complex web of national identity, telecom infrastructure, and digital strategy. Though not a formal ITU prefix, its meaning runs deep in how billions connect each day. Behind every call, text, and data packet lies a structured universe of codes, with 0063 representing one vital node in the world’s most intricate communication network.


Related Post

The Ultimate Guide to Masters of Creativity in NBA 2K23 Arcade Edition Offline Mode
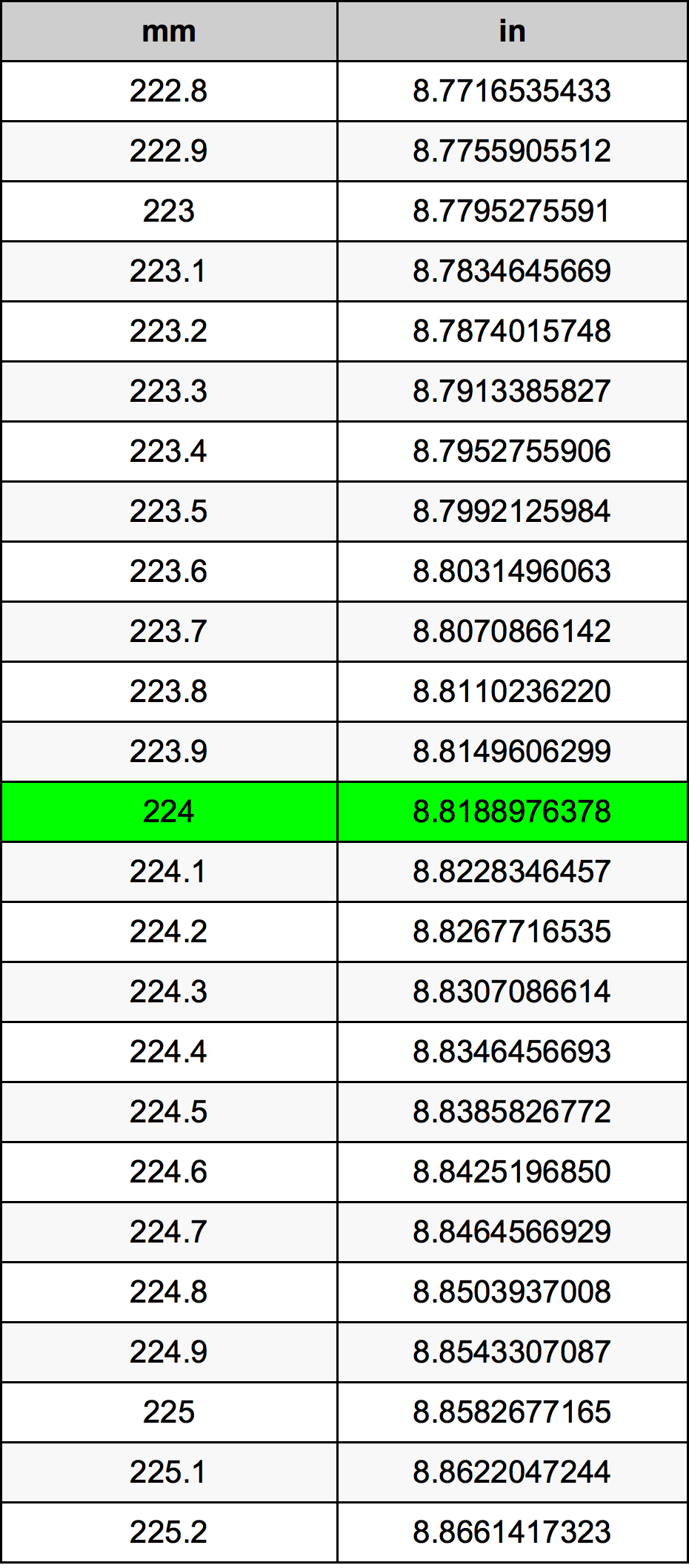
Precision in Every Inch: How 7x32 Inches Equals 224 MM and Reshapes Global Measurement Standards

How to Decode the LLC on Your Bank Statement: Understanding Fid Bkg Svc Moneyline Data

Unmasking The Dark Side: Fourth Wing’s Hidden Evil Characters Exposed

