What Is The Chemical Formula For Glucose?
What Is The Chemical Formula For Glucose?
The humble molecule behind the energy that powers life itself—glucose—holds a simple yet profound place in biochemistry. Defined by its precise chemical formula, C₆H₁₂O₆, glucose serves as the primary sugar used by nearly all living organisms for immediate energy production. This carbohydrate, classified as a monosaccharide, forms the structural and energetic foundation of cellular metabolism, underpinning everything from muscle contraction to brain function.
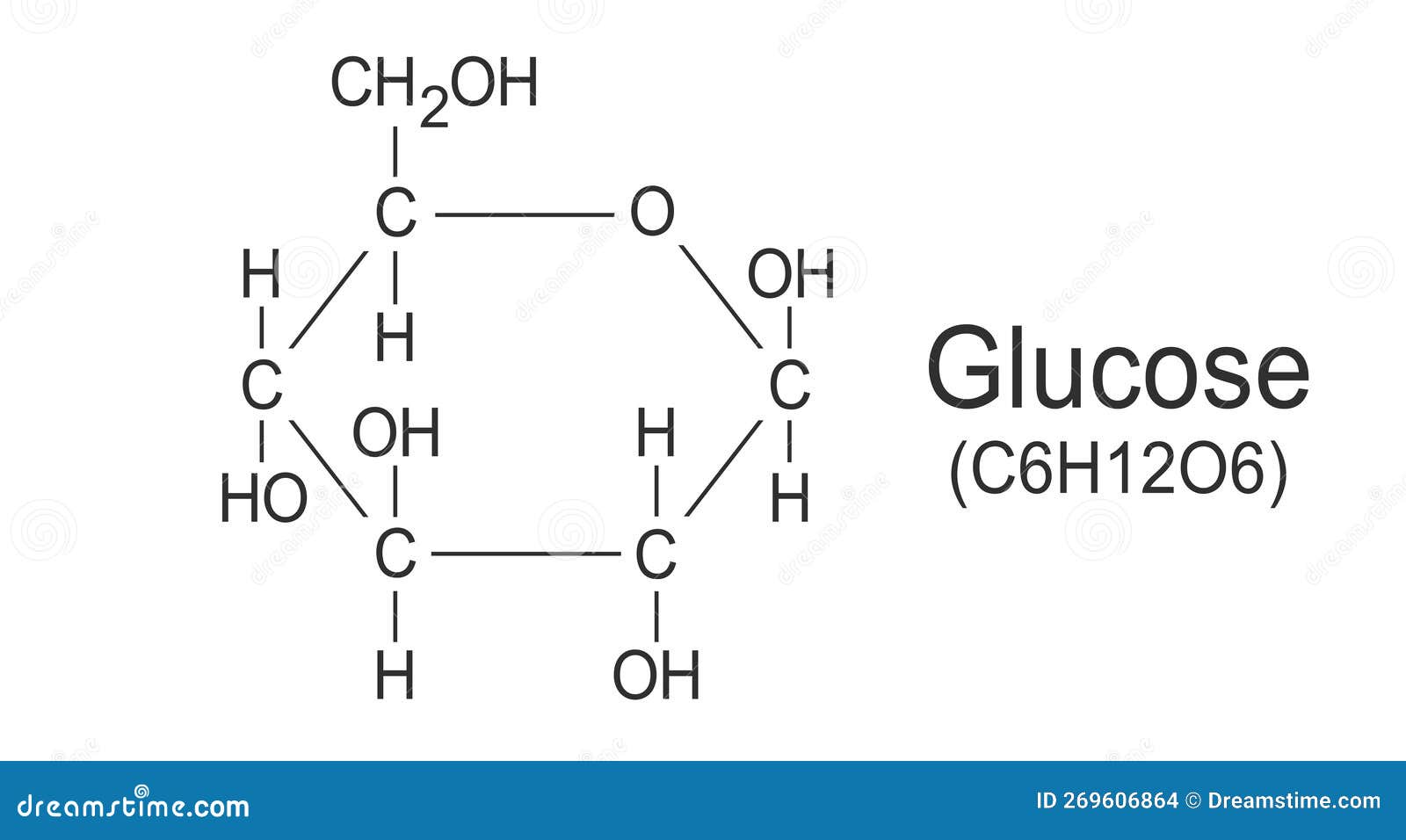
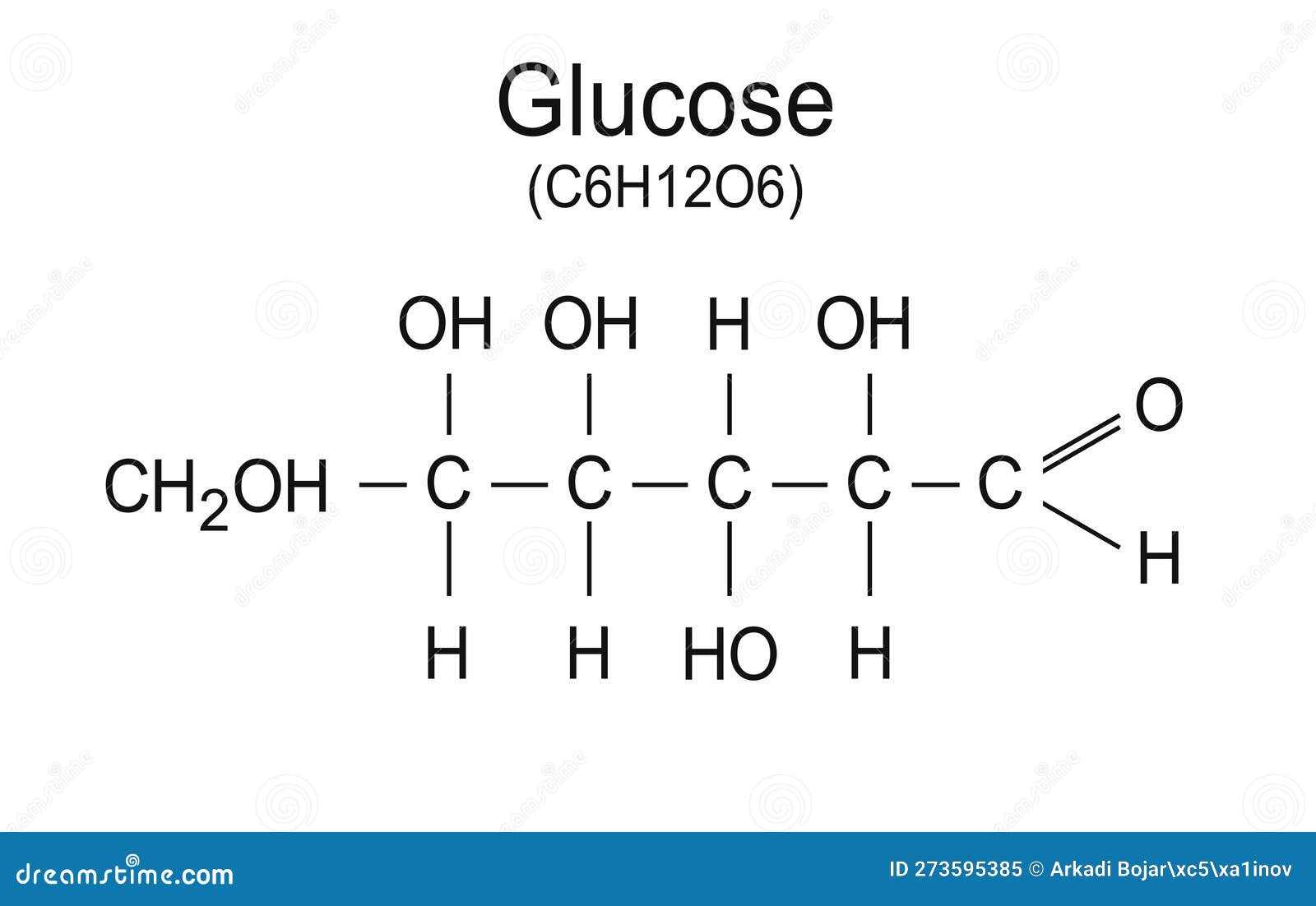
Understanding its formula goes beyond memorization—it reveals the balance of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that enables glucose to fuel life at the molecular level. Glucose’s chemical structure reveals a masterpiece of organic design. With six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms arranged in a stable ring configuration, its formula C₆H₁₂O₆ encapsulates both simplicity and biochemical significance.
Each carbon atom bonds with hydrogen and oxygen in configurations that allow glucose to serve dual roles: as a fuel molecule and as a precursor for more complex carbohydrates. Unlike polysaccharides such as starch or cellulose—which consist of long glucose chains—this monosaccharide exists in a compact, energetic form ideal for rapid cellular uptake and use. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen—twice as many hydrogens as oxygens—hints at glucose’s high energy content, a hallmark of its biological role.
Why The Formula Matters in Science and Health The formula C₆H₁₂O₆ is far more than a chemical notation—it’s a key to understanding metabolism, nutrition, and disease. In biochemistry, this precise composition explains how glucose interacts with cellular pathways. When consumed, glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells, where it undergoes glycolysis, a process that converts its structure into usable energy in the form of ATP.
Because of its consistent molecular makeup, scientists can predict and measure how glucose influences insulin response, blood sugar regulation, and energy metabolism across species. Nutritionists rely on knowing glucose’s formula to evaluate dietary impact. For athletes, the balance of glucose intake directly affects endurance and recovery, while for diabetics, tracking glucose levels is critical to managing blood sugar.
“Glucose is the linchpin of metabolic efficiency,” notes Dr. Elena Marquez, a biochemist at the Institute of Molecular Nutrition. “Its chemical formula—C₆H₁₂O₆—represents the precise blueprint that makes it such a vital energy source.
Without this specific ratio, glucose would lose the capacity to fuel life’s fundamental processes.” Beyond human physiology, glucose’s chemical structure plays critical roles in plant biology and industrial applications. Plants synthesize glucose during photosynthesis using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water, converting carbon from CO₂ into a storable, transportable form. This made-to-order structure enables efficient energy storage in tissues, supporting growth and development.
Meanwhile, the stability and versatility of C₆H₁₂O₆ make glucose a cornerstone in food science, pharmaceuticals, and fermentation industries—from sweetening agents to precursor molecules in drug synthesis. Even in structural biology, glucose’s formula influences molecular recognition. The arrangement of atoms grants glucose specific binding affinities with enzymes and receptors, mediating processes as delicate as nerve signal transmission or immune cell activation.
While glucose itself rarely acts alone—often forming polymers or combining with other sugars—its core structure ensures compatibility and functionality across biological systems.
In essence, C₆H₁₂O₆ is more than just a chemical formula; it is the molecular key to energy, life, and health. Its simplicity belies a profound complexity that underpins metabolism, nutrition, and biotechnological innovation.
From fueling our cells to shaping dietary science, glucose’s formula stands as a testament to nature’s precision. Understanding this fundamental structure deepens our appreciation of biological systems—and empowers scientific progress in medicine, agriculture, and beyond.


Related Post

Halle Berry Net Worth The Glamorous Journey of an Iconic Actress

Utah Jazz Injury Report: Tracking Key Musculoskeletal Setbacks Amid Training Season

Top Up Robux Easily: Your Guide to Iocara and Beyond
Unveiling Jonathan Roumie’s Salary for ‘The Chosen’: A Premium Bet Behind the Gospel Series

