The Derivative of lnX: Unlocking Insights in Mathematics and Applications
The Derivative of lnX: Unlocking Insights in Mathematics and Applications
Among the most foundational functions in calculus, the natural logarithm—$ \ln x $—plays a pivotal role in modeling growth, decay, probability, and entropy, among other phenomena. Its derivative, $ \frac{d}{dx}[\ln x] = \frac{1}{x} $, is not only elegantly simple but also remarkably powerful across scientific and engineering disciplines. Understanding this derivative reveals deeper patterns in change, optimization, and information theory, making $ \frac{1}{x} $ a cornerstone of applied mathematics.
From finance to thermodynamics, this expression underpins models that shape modern technology and economic systems.
Mathematical Foundation of lnX and Its First Derivative
At the heart of exponential and logarithmic relationships, $ \ln x $ is defined as the integral of $ \frac{1}{t} $ from 1 to $ x $, or equivalently as the inverse function of $ e^y $. When researchers analyze how quantities evolve relative to their scale—particularly in return-per-time or entropy-based contexts—the derivative $ \frac{1}{x} $ emerges consistently. This simple expression encapsulates the idea that relative change diminishes as $ x $ increases—a core principle in logarithmic scaling.
The antiderivative of $ \frac{1}{x} $ over positive real numbers yields $ \ln|x| $, with the absolute value reflecting domain considerations where $ x > 0 $. This relationship forms the backbone of integral calculus involving logarithms and enables accurate modeling of continuously compounding processes, such as interest growth or population dynamics.
Critical Properties: Continuity, Differentiability, and Domain Constraints
For $ \frac{d}{dx}[\ln x] = \frac{1}{x} $ to hold, $ x $ must lie strictly within the domain $ (0, \infty) $. At $ x = 0 $ and $ x < 0 $, the logarithm is undefined in the real domain, rendering $ \ln x $ non-differentiable.
Similarly, discontinuities and undefined behavior outside this interval prevent the formula’s application. This careful boundary condition underscores the necessity of domain awareness in mathematical modeling, especially when estimating rates of change in real-world systems. Despite its apparent simplicity, the expression $ \frac{1}{x} $ is foundational to more complex derivatives.
For instance, applying the chain rule to $ \ln(f(x)) $, where $ f(x) $ is a smooth function, produces $ \frac{f'(x)}{f(x)} $—a formula indispensable in life sciences and financial derivatives calculus. The derivative’s structure also appears in information entropy, where $ -\ln p(x) $ quantifies unpredictability, linking mathematical theory directly to data science applications.
Real-World Applications of the Derivative: From Calculus to Economics
In finance, the derivative of $ \ln x $ underpins the concept of continuously compounded interest, where $ e^{rt} $ emerges as the growth function. The rate of change of logarithmic returns approximates short-term market volatility, allowing traders and risk managers to quantify uncertainty in asset performance.
“The log return,” $ \ln \left( \frac{P}{P_0} \right) $, measures relative change without skew from multiplicative fluctuations—essentially relying on $ \frac{1}{x} $-type dynamics.
Thermodynamics similarly leverages this derivative in modeling entropy. From Boltzmann’s $ S = k \ln W $, where $ W $ is the number of microstates, the $ \ln x $ behavior informs how macroscopic disorder scales with system complexity. Small perturbations in $ x $—such as temperature shifts—trigger predictable changes in entropy, governed by $ \frac{1}{x} $’s sensitivity properties.
In machine learning, gradient-based optimization often uses log-likelihood gradients, where $ \ln x $ derivatives influence loss landscape geometry.
Automated systems, from recommendation engines to natural language models, depend on precise gradient computations rooted in $ \frac{d}{dx}[\ln x] $ to adjust parameters efficiently.
Compiling Examples and Comparative Insights
Consider a population growing continuously at rate $ r $: $ P(t) = P_0 e^{rt} $. The relative growth rate, $ \frac{d}{dt}[\ln P(t)] = r $, is constant—this stability stems directly from $ \frac{1}{P(t)} \cdot \frac{dP}{dt} = r $. Here, $ \frac{1}{x} $ ensures proportional change remains invariant to absolute scale.
In contrast, linear growth $ g(t) = at + b $ yields a derivative $ \frac{d}{dt}[\ln g(t)] = \frac{a}{at + b} $, which decays with $ t $. The shift from constant relative to fixed absolute growth reflects how $ \frac{1}{x} $ shapes dynamic behavior fundamentally: logarithmic scaling preserves proportionality, while linear scaling does not.
The Indispensable Role of lnX’s Derivative in Modern Science
Beyond isolated equations, the derivative $ \frac{1}{x} $ exemplifies a recurring theme in scientific progress: simplicity birthing profound utility. Its role in transforming multiplicative processes into additive rates enables modeling across scales—from cellular metabolism to stock market fluctuations.
“It’s not just a number; it’s a lens,” says Dr. Elena Torres, applied mathematician at MIT, “allowing us to see patterns in chaos where raw data fails.”
Whether optimizing neural networks, calculating thermodynamic limits, or assessing financial risk, $ \frac{d}{dx}[\ln x] = \frac{1}{x} $ remains a silent architect. This elegant expression captures how relative change manifests mathematically, offering clarity in fields where precision is paramount.
Its enduring relevance confirms logarithms and their derivatives as linchpins of quantitative reasoning.
In every field from physics to economics, the fundamental truth endures: understanding how functions evolve—via $ \ln x $ and its derivative—illuminates the mechanics of growth, decay, and uncertainty. The formula $ \frac{1}{x} $ is more than a calculus result; it’s a gateway to insight, shaping how we model reality and extract meaning from data.
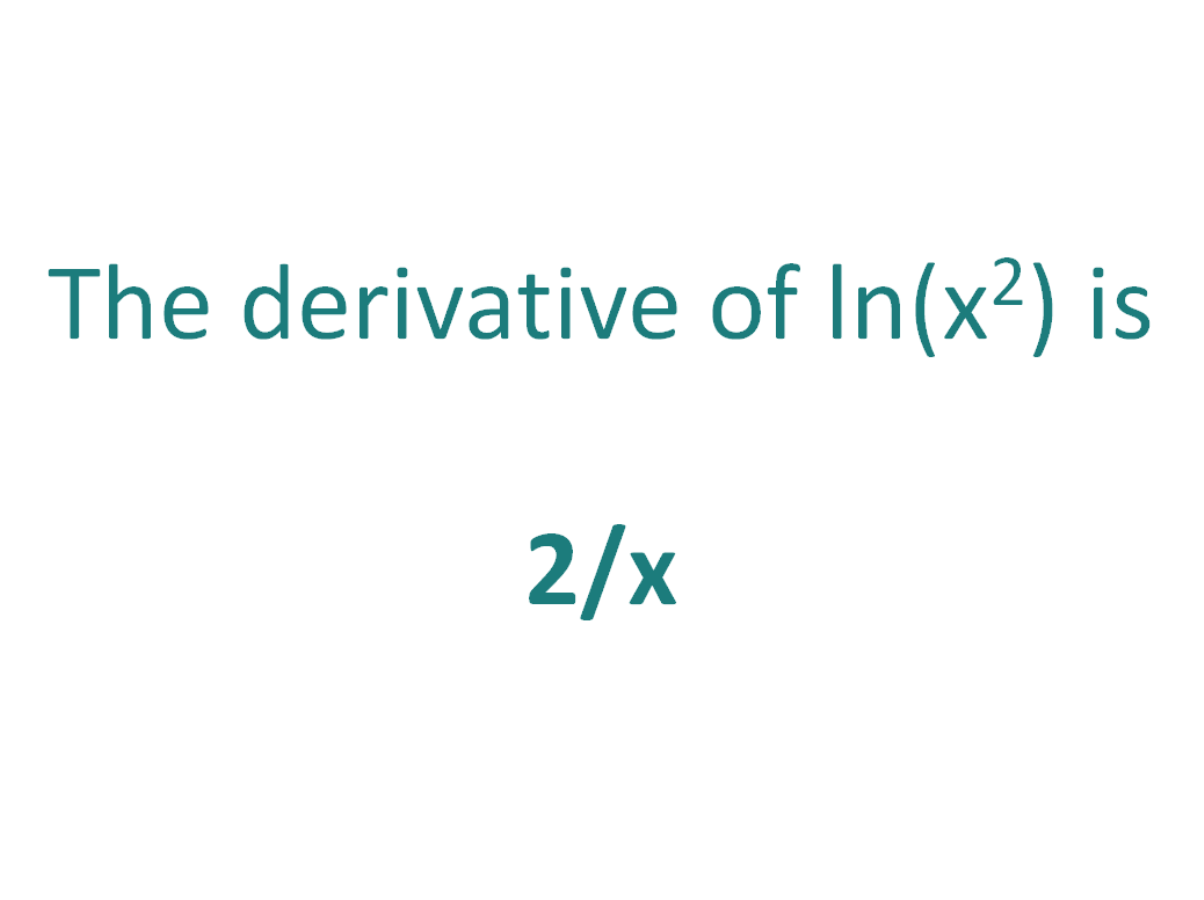
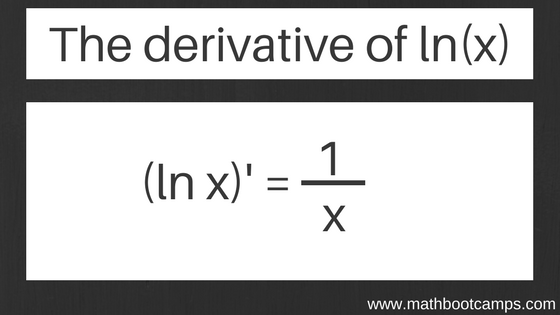
![What is the Derivative of lnx^2 [Solved] - iMath](https://www.imathist.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Derivative-of-lnx^2.webp)

Related Post

Christian Bales Grips the Driver’s Seat in a Ford V Ferrari — A Masterclass in Precision and Grit

Did Kamala Harris Pass The Bar? The Legal Foundation Behind a Tenured Senator

Combat Initiation: The Critical Moment That Decides Battle Outcomes

Diesel Kubota Tractor Ultimate Guide and Repair Tips: Master Maintenance, Diagnose Fast, Keep Productivity Soaring

