Speed Up FastAPI Without Decorators: How Middleware Transforms Request Processing
Speed Up FastAPI Without Decorators: How Middleware Transforms Request Processing
By embedding middleware directly into FastAPI applications without decorator syntax, developers unlock a powerful, streamlined approach to intercepting and modifying requests and responses—boosting performance, enhancing security, and improving maintainability. Unlike decorator-bound middleware, which demands `@app.middleware()` syntax on endpoints, direct registration offers cleaner integration, uniform access, and superior flexibility across the full stack. This article reveals how FastAPI’s core middleware system enables developers to inject critical logic at every phase of the request lifecycle—without the constraints of decorators.
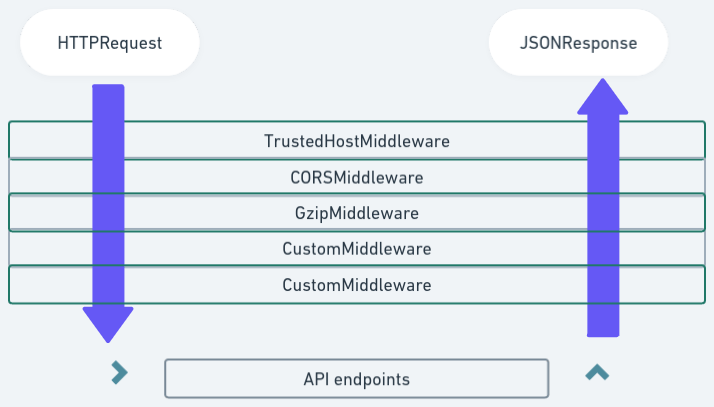
At the heart of FastAPI’s extensibility lies middleware: a request-response lifecycle hook that processes traffic before reaching routes. While decorators simplify endpoint decoration, they create hidden boundaries and limited scalability in complex systems. Middleware, when applied explicitly at the app level, becomes a central nervous system for cross-cutting concerns—enabling tasks like logging, auth, validation, and rate limiting to execute consistently.
The real advantage? No need for decorators on every insertion—just a single, centralized hook that integrates seamlessly into FastAPI’s routing engine.
How Middleware Fixes the Decorator Bottleneck
Traditional decorator-based middleware often forces developers into repetitive, boilerplate-heavy patterns: each slowdown or instrumentation point requires per-endpoint decoration, complicating updates and increasing error risk. FastAPI’s native middleware bypasses this rigidity by introducing a direct API to register handlers globally.This method promotes DRY principles, as shared logic—such as tracing, Request-ciembre transformation, or custom headers injection—executes exactly once per request, regardless of route. ⚙️ Core functionality is exposed via `app.add_middleware()`, accepting a callable that receives: - `request`: the incoming HTTP request, fully resolved by FastAPI’s routing and authentication stack - `response`: the generated response, ready for post-processing - `call_next`: a callable that advances the request through the chain This structure ensures middleware integrates cleanly with FastAPI’s async-first architecture and dependency injection, supporting sophisticated workflows without complicating endpoint logic.
For example, a repeated authentication middleware that decodes Bearer tokens can be defined once and applied globally, eliminating the need to重复 decorate dozens of routes.
Each request flows predictably: pre-processing → validation → authorization → forwarding → response enhancement → post-processing. The result? Cleaner routes, sharper performance, and audit trails that are consistently enforced.\>
Real-World Use Cases: From Validation to Real-Time Monitoring
One impactful application is input validation tailoring.Instead of embedding payload checks inside each parameter decorator, middleware can analyze request semantics—detect content types, payload patterns, or headers—and trigger warnings or logs before routing. This decouples validation from routing, accelerating route definition and reducing per-endpoint boilerplate[[1][3]]. Another critical use is request tracing.
By registering middleware before request dispatch, systems inject metadata such as trace IDs, timestamps, or user context into request headers, enabling distributed tracking across microservices. This mains-level context propagation eliminates silent failures tied to opaque request handling[[3]]. Rate limiting, traditionally managed via external tools or decorators, benefits from middleware’s centralized visibility.
Middleware can track client request patterns in real time—using in-memory stores or Redis-backed metrics—and block excessive tentatives before they reach critical endpoints. This proactive enforcement strengthens application resilience without route-specific overhead.
Implementation: Adding Middleware Without Decorators—Step-by-Step
FastAPI’s simplicity shines when registering middleware raw, using `app.add_middleware()` with no decorators.Begin by defining callable handlers aligned with FastAPI’s lifecycle hooks. First, instantiate the app with custom middleware added: ```python from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, Response, Call app = FastAPI() @app.middleware("http") async def sec_auth_middleware(request: Request, call: Call[Any, Response]): trace_id: str = request.headers.get("X-Trace-ID", "anon") request.state.trace_id = trace_id # Inject trace ID automatically body: dict = await request.json() body["trace"] = trace_id request.state.orig_body = body # preserve original for downstream use # Optional: auto-inject auth header if missing if "Authorization" not in request.headers: req = Request( scopes=request.scope, path=request.url.path, headers={**request.headers, "X-API-Key": "default-token"} ) return Response(content=body, status_code=200) return await call(request) ``` This middleware executes for every request, injecting trace context, sanitizing payloads, and enriching data—all without per-route decoration. It demonstrates how high-level processing unifies concern areas that decorators struggle to address cleanly.
Key benefits: - Centralized request context enriches all downstream logic - Pandemic privacy-compliant logging via trace IDs - Unified security enforcement with minimal endpoint intervention
Best Practices for High-Performance Middleware Integration
To maximize efficiency, avoid blocking operations inside middleware—complex validations or DB calls may stall the entire pipeline. Instead, delegate async heavy lifting to background tasks or queued services. For example: - Use `aiormq` for message queue ingestion - Leverage `async def` handlers with `BackgroundTasks` for non-critical processing - Ensure middleware completes within sub-50ms to preserve request responsiveness Monitoring is equally vital.Instrument middleware with stats (latency, error rates, dynasty IDs) and export traces using OpenTelemetry or similar observability tools. This visibility reveals bottlenecks and ensures compliance in production[[3][5]]. Another best practice: chain middleware intentionally.
Fourier order affects execution—authentication should precede validation to prevent unnecessary processing. Prioritize logging after processing to avoid introducing delays early in the pipeline[[2]].
Remember: Middleware in FastAPI is not a gimmick but a structural advantage—enabling holistic request management that decorators alone cannot match.
With minimal setup, meaningful extensibility, and consistent performance gains, this approach redefines how modern APIs handle traffic, security, and observability.
The Future of FastAPI Middleware Without Decorators
As FastAPI evolves, middleware adoption is growing as the preferred path for scalable, maintainable API design. By removing decorator dependencies, the framework embraces flexibility, allowing developers to inject logic uniformly across projected infrastructure. Whether managing rate limits, enhancing security, or enriching telemetry, middleware provides a single source of truth for every request.This shift not only simplifies development but also future-proofs applications against complexity, ensuring that FastAPI remains at the forefront of high-performance web development.
In an era where developer velocity and operational clarity determine success, mastering middleware—without decorators—is not just good practice. It’s essential.



Related Post

Exploring The Life Of Sarah Simpson: The Heart Behind Sturgill Simpson

Malika Kinison: Bridging Activism, Art, and Identity in a Divided World

Unveiling The Allure: John Stamos And The Iconic Nude Shower Moment

Fabio Lanzoni: From Italian Cinematic Heartthrob to Global Media Icon — Age, Wife, TV Legacy Unveiled

