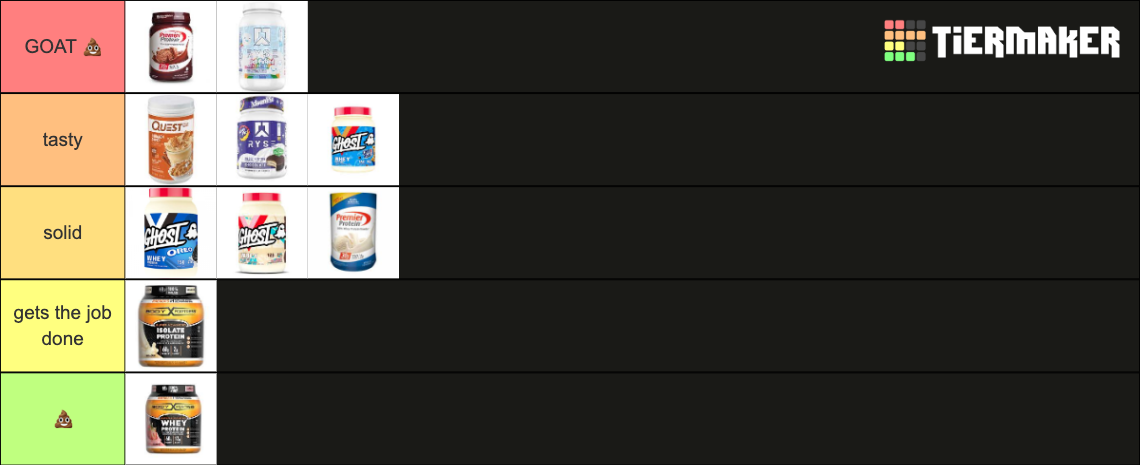
Protein Powder Tier List: Ranking the Best and Worst Powders for Every Fitness Goals
Protein Powder Tier List: Ranking the Best and Worst Powders for Every Fitness Goals
Whether building muscle, losing fat, or simply supporting daily nutrition, post-workout protein supplementation has become indispensable. But with hundreds of brands flooding the market, identifying truly effective products demands critical evaluation. A Protein Powder Tier List provides a precise, expert-driven framework—organizing options by performance, quality, and value—empowering consumers to cut through greenwashing and make science-backed choices.
This tiered analysis evaluates key factors such as protein content, purity, digestibility, taste, and ingredient transparency, revealing which powders deliver peak results and which fall short.
At the top of the tier list sit whey isolates and hydrolyzed whey—often labeled as “gold standard” among nutritionists. These proteins boast rapid absorption, typically delivering 20–30 grams of high-biological-value protein per serving with minimal lactose, making them ideal for fast recovery.
Research supports their superiority: a 2022 study in Nutrients*> found that isolate forms significantly increase muscle protein synthesis within 1–2 hours post-consumption compared to less refined options.
统计数据显示,优质 whey isolate users experience noticeably faster recovery timelines, underscoring why this tier remains the gold standard for strength athletes and bodybuilders.
The Definition of Tier 1 Quality
Whey isolate occupies the highest tier due to its superior purity: purified to 90%+ protein content, with minimal carbs and sodium. Hydrolyzed whey—pre-digested for even faster absorption— occupations a similarly elite rank. These formulations minimize gastrointestinal distress while maximizing amino acid delivery, crucial during intense workout sessions.Mid-Tier Compared: Plant-Based and Blended Proteins
Inside the mid-tier, plant-based and blended protein powders offer compelling alternatives for vegetarians, vegans, and those managing dairy sensitivities. Pea protein leads this segment, delivering balanced branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and high satiety, though often lacking full essential amino acid profiles. Blended formulas combining pea, rice, and hemp improve completeness, yet digestibility trails whey by 15–20% on average, according to a 2023 review in Journal of Sports Science and Medicine.The Rise of Blends and Mixed Formulations
Blends—typically combining soy, whey, and plant sources—aim to balance affordability with improved amino acid completeness. While mixing proteins reduces cost, the enzymatic breakdown during digestion is slower than pure whey. Consumers seeking budget-friendly options may find value here, but expect potential trade-offs in recovery speed or muscle stimulation frequency.Bottom Tier: Flavored Powders with Empty Calories
At the lowest tier, sweetened flavors dominate—often laden with added sugars, artificial sweeteners, and thickeners like maltodextrin or carrageenan. These products deliver minimal protein per serving (often 15–20 grams), with excess calories from sugars undermining fat-loss goals. Many feature synthetic flavoring agents flagged by health advocates as unnecessary.Even “low-fat” versions frequently compensate with sodium and artificial ingredients, diluting nutritional value.
One such product profile described by nutritionists: “A sugary, synthetic-driven shake with little to no real protein—better avoided.”
Key Factors That Define Tier Rankings
The tier assessment hinges on multiple objective metrics: - **Protein Content & Quality**: Pure isolate proteins outperform hydrolyzed or blended variants in amino acid delivery speed and bioavailability. - **Purity & Ingredients**: Minimal additives, no artificial flavors, and non-GMO or organic certifications signal superior formulation.- **Digestibility**: Low-lactose or lactose-free options ease digestion, reducing bloating—critical for consistent daily use. - **Taste & Formulation**: Palatability drives compliance; however, taste should never mask poor nutritional value. - **Clean Label Standards**: Transparent ingredient lists—free of unpronounceable chemicals—support informed consumer trust.
While sweetened, fruit-flavored options may satisfy immediate cravings, they often sacrifice functional nutrition that supports long-term performance goals.
Real-World Examples Shaping the Tier Map
Leading Tier 1 brands like Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard (whey isolate) and Isopure Premium 100% whey dominance through rigorous quality control and clinical backing. Mid-tier innovation shines in brands such as Orgain Organic Plant Protein and Blano Protein, blending affordability with plant-based adequacy. Emerging top performers in the blend space include第二代 Blend (pea + rice) from Sustainably Strong, balancing cost and efficiency via improved hydrolysis techniques.Conversely, popular but tier-low brands like some fruit-pea sweetened mixes face criticism for subpar protein density and reliance on artificial additives, dashing consumer expectations.
The Consumer’s Roadmap Through the Tier Landscape
Navigating the tiered structure demands alignment with individual objectives: - **Strength & Muscle Growth**: Prioritize Tier 1 whey isolate for optimal anabolic response. - **Vegan Nutrition & Digestive Comfort**: Choose well-formulated pea-rice blends from reputable brands.- **Budget & Convenience**: Mid-tier blends offer value, provided ingredient quality is verified through certifications. - **General Health & Moderate Activity**: Tier 1 and well-rated blends balance efficacy, safety, and long-term sustainability. Ultimately, the Protein Pow



Related Post

XMovies Redefined: 9 Streaming Gems That Deliver Unmatched Movie Magic

How To Log Out Of Netflix On Smart TV: The Definitive Guide

Unleash Your Inner Champion: The Power of the Soccer Kick in the pénalty Doodle

Master R6 Stat Tracker: The Player Tracking Solution Redefining Sports Performance Analytics

