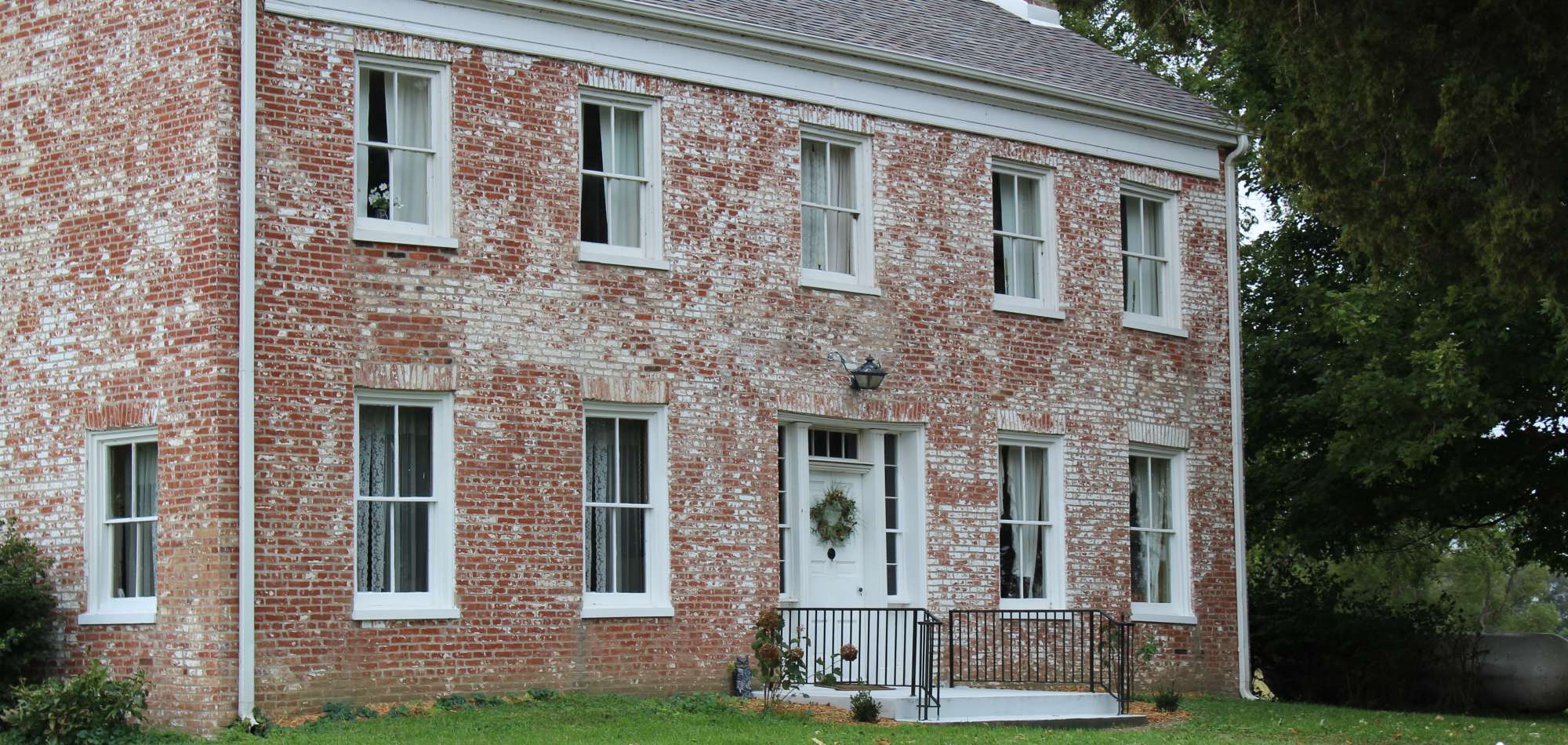
Jacksonville Hole: Nature’s Hidden Gem and Jacksonville’s Underground Playground
Jacksonville Hole: Nature’s Hidden Gem and Jacksonville’s Underground Playground
Nestled deep within the heart of Jacksonville, Florida, Jacksonville Hole stands as both a mysterious natural curiosity and an unexpected urban retreat—a subterranean sinkhole cloaked in lush greenery, secret histories, and vibrant community engagement. This geological formation, more than a simple depression in the earth, has become a multifaceted destination where geology, ecology, recreation, and local heritage converge. From its formation eons ago to its modern-day role as a nature sanctuary and outdoor adventure zone, Jacksonville Hole exemplifies how preserved natural wonders can thrive in the pulse of a major city.
独特的地质起源与生态奇迹 Formed through karst processes typical of Florida’s limestone bedrock, Jacksonville Hole emerged over thousands of years as acidic groundwater eroded soluble rock, creating a dramatic sinkhole roughly 150 feet in diameter and 75 feet deep. This natural cavity, now partially filled with fresh water and ringed by dense high-hat hammock, supports a rare micro-ecosystem. The shaded, moisture-rich environment nurtures native flora such as wild ginger, ferns, and ancient oak trees, while attracting diverse wildlife including barreling toads, rail birds, and rare salamander species.
“Walking over Jacksonville Hole feels like stepping into a living cathedral of geology,” says Dr. Elena Márquez, a geologist with Florida State University’s Department of Earth Sciences. “The strata exposed here tell a deep-time story—layer by layer, you can observe millions of years of subsurface transformation.” From Natural Reserve to Urban Oasis Once a remote and inaccessible feature, Jacksonville Hole has undergone a transformation into a publicly accessible nature preserve.
Jacketed with boardwalks and guided trails, the site now welcomes hikers, birdwatchers, and nature photographers year-round. Its elevation—over 50 feet below the surrounding terrain—offers unique microclimatic conditions that buffer urban heat and stabilize local hydrology, supporting stormwater retention and reducing runoff into nearby waterways. The area’s ecological health is carefully monitored through partnerships between the Jacksonville Coastal Conservancy and local universities.
Recent surveys identified over 37 bird species utilizing the sinkhole’s wetlands and forest canopy, making it a vital stopover for migratory routes. Conservationists emphasize that even small sinkholes like Jacksonville Holiday serve as ecological linchpins in fast-developing regions. Recreational Access and Community Connection Accessibly positioned within a 10-minute drive from downtown Jacksonville, the site balances ease of access with a sense of isolation.
A 0.6-mile loop trail winds through the sinkhole’s rim and submerged sinkhole floor, featuring interpretive signs detailing geology, hydrology, and native species. Nighttime visits are popular for stargazing by larger groups conducting educational programs. This space is not merely a nature preserve—it’s a community anchor.
Local groups organize monthly clean-up days, native gardening workshops, and school field trips that foster environmental stewardship among Jacksonville’s youth. “It’s where neighbors gather, kids learn, and adults find peace,” notes Carlos Ruiz, a volunteer ranger and long-time resident. “Jacksonville Hole isn’t just rock and water—it’s a living classroom and gathering place.” Preserving Heritage Beneath the Surface Deeper layers of history enrich the sinkhole’s story.
Prehistoric artifacts found near the rim suggest At oferta组装됥한集落 once thrived along its edges, relying on its springs and fertile soil. Early 20th-century maps reference Native Seminole use of nearby water sources, though physical evidence within the sinkhole itself remains limited, underscoring the need for archaeological sensitivity. Today, protective zones surround sensitive areas to prevent contamination from urban encroachment, ensuring that both cultural and natural resources endure.
Monitoring systems track water quality and structural stability, critical for maintaining safety amid Florida’s dynamic weather patterns.
Ecological Significance: A Biodiversity Hotspot in an Urban Landscape
Jacksonville Hole defies expectations as more than a scenic curiosity—it functions as a resilient ecological island within a sprawling metropolitan region. Its stratified ecosystem supports species adapted to intermittent wetlands and shaded forest floors, many of which struggle in surrounding developed zones.Studies show the sinkhole’s vegetation acts as a biological corridor, linking fragmented green spaces and enabling species movement across Jacksonville. Amphibian populations, particularly the critically sensitive Florida zur continual alert. Conservation initiatives now use the site as a model for urban sinkhole rehabilitation, proving such features can serve dual purposes: environmental restoration and public engagement.
Safety, Access, and Advisories for Visitors
While visually striking, Jacksonville Hole demands cautious exploration. Boardwalks circle the perimeter, preventing accidental falls into the 75-foot depression. Water within is deep and hazardous, with fluctuating clarity due to seasonal rainfall and subterranean seepage.Swimming or wading is strictly prohibited. Visitors are advised to follow marked trails, carry proper footwear, and check weather forecasts before visiting. Rangers and trail guides are available during peak hours— Friday through Sunday—to provide safety checks and interpretive commentary.
Early morning or twilight visits minimize heat exposure and offer prime wildlife observation opportunities. The site operates under a low-impact policy: litter-free entry, no drone flights, and no collection of flora or fauna. These measures protect both human safety and ecological integrity.
Future Vision: Jacksonville Hole as a Model for Urban Natural Preservation
As Jacksonville continues to grow, Jacksonville Hole stands as a testament to the power of integrating natural heritage into urban planning. Its layered identity—as geologic formation, ecological sanctuary, cultural landmark, and public space—offers a replicable blueprint for cities worldwide. Local officials and environmental advocates envision expanded educational programming, possibly including a small nature center and guided cave-like cave tours (where permissible) to deepen public connection.Ongoing research into hydrological patterns and biodiversity internalization could guide climate adaptation strategies, ensuring sinkhole ecosystems remain resilient. In a world where urban expansion threatens natural landscapes, Jacksonville Hole emerges not just as a hole in the ground, but as a living archive—of time, life, and community. It challenges the notion that nature and city life must be segregated.
Instead, it invites residents to see beneath their feet, beneath their skyline, and discover a wild, enduring heart hidden just south of downtown Jacksonville.




Related Post

Iyasakura: Unveiling the Serene Beauty and Timeless Legacy of This Ancient Japanese Blossom
Top 10 Richest Nations: Where Global Wealth Concentrates in the Modern Economy

Circles: The Universal Shapes Shaping Nature, Design, and Human Culture

How Israel Makes Money: A Dynamic Engine of Innovation and Global Trade

