Inside Alaska’s Timekeeper: How Anchorage, Alaska Time Zone Shapes Life on the Frontier
Inside Alaska’s Timekeeper: How Anchorage, Alaska Time Zone Shapes Life on the Frontier
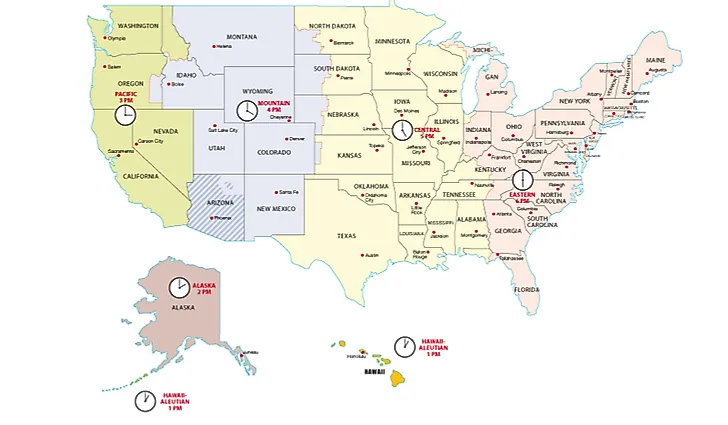
In the vast, snow-laden expanses of Southcentral Alaska, the rhythm of daily life is set by a clock uniquely attuned to the rhythms of nature—Anchorage Alaska Time Zone, a 9 UTC offset segment running from earliest spring to latest fall. Spanning roughly March through October, this zone governs everything from school start times in suburban neighborhoods to the launch windows of cargo flights delivering critical supplies to remote villages across the Inside Passage. Unlike the contiguous United States, where time is a uniform grid, Alaska’s time zones reflect the state’s geographic isolation and environmental extremes, with Anchorage anchoring a busy corridor where aviation, fishing, tourism, and indigenous cultures converge—all synchronized to a single, unifying pace.
> “Anchorage is the heartbeat of the region,” says Elena Torres, an urban planner with the Municipality of Anchorage. “Our day-to-day functions—from ferry schedules to emergency response timings—depend entirely on precise timekeeping tied to this time zone.” Anchorage operates on Pacific Standard Time (PST) from September through November and shifts to Pacific Daylight Time (PDT) in March when daylight saving takes effect. This biannual flip aligns the city with Pacific Time more closely, extending daylight hours during the long Alaskan summers but introducing confusion in winter months.
For residents accustomed to early darkness by late fall, the switch can disrupt routines—mail deliveries delayed, transit runs later, and fitness schedules thrown off.
One of Anchorage’s defining characteristics is its extreme seasonality, and the time zone amplifies this variability. From sunrise at 4:14 AM in December to midnight sun lasting until mid-July, daily light patterns shift dramatically.
“Time isn’t just a number here—it’s a survival tool,” said벌ivity Nakashima, a subsistence hunter and longtime Anchorage resident. “We plan our trips by the clock and the sun, knowing that every hour counts when traveling a snowmobile across the backcountry or fishing in the Bering Sea.”
The time zone also plays a critical logistical role in Alaska’s transportation network, where timing is often the difference between punctuality and peril. Commercial airlines, cargo carriers, and medical evac jurisdictions rely on coordination within the —9 UTC zone to schedule flights, docks, and response teams efficiently.
In Anchorage, the busiest airport—home to over 2 million passengers annually—coordinates international arrivals with mainland hubs using this consistent, predictable time reference. > “Time zones give us a shared reference in a landscape where distances are vast and roads sparse,” explains Captain Rajiv Mehta, a pilot with Alaska Seaport Services. “Anchorage’s time zone acts as the anchor point for flight schedules, search-and-rescue operations, and cargo logistics.
Without it, coordination would unravel.” Behind this seamless operation lies Alaskan time zone governance, managed jointly by the Alaska Time Zone Authority and federal aviation standards. Unlike many states, Alaska experiments with daylight saving differently—delaying its switch each March and advancing in September—fine-tuning the zone’s alignment with natural light rather than clock shifts. This approach supports outdoor recreation industries, where hiking, fly fishing, and wilderness tourism thrive in extended daylight.
The impact extends beyond convenience, shaping cultural identity and community life. In neighborhoods like Midtown and Hill Top, schools begin instruction before sunrise in winter, kids skating or sledding often racing against the clock as the first bell rings. Businesses adjust staffing, shift cycles, and delivery windows to match consistent operating hours.
Indigenous communities use time zones to preserve language and tradition—scheduling cultural gatherings and storytelling circles at optimal hours, reinforcing connection across generations.
Technological adaptation has further embedded the time zone into daily life. Smart home systems sync to Anchorage Time, voice assistants recalibrate schedules, and businesses across retail, healthcare, and hospitality automate time-based announcements.
In remote areas near the Kenai Peninsula, satellite-based time distribution ensures even off-grid cabins maintain alignment with central services.
Yet, challenges persist. Year-round daylight in summer blurs boundaries between work and rest; winters bring near-constant darkness that strains mental health and disrupts circadian rhythms.
The biannual clock shift, though minor in minutes, adds cumulative stress, especially for healthcare providers and transportation crews. Communities increasingly advocate for flexible scheduling and public education to ease the transition, emphasizing the time zone’s deep integration into Alaskan life.
More than a technical necessity, Anchorage’s time zone is a cultural artifact—one that balances modern infrastructure with the raw, unyielding environment of Alaska.
It structures commerce and community, protects safety, and honors the state’s unique geography. As climate change alters sea ice, migration patterns, and seasonal rhythms, the time zone remains a quiet but vital thread connecting people to place, opportunity, and resilience. In Alyeska—the state’s official Alaska name—time is not just measured here by the tick of a clock, but lived by its pulse, its sky, and its people, all synchronized to the quiet authority of


Related Post

Ted Cruz’s Texas Flood Trip Sparks Scrutiny Amid Israel Visit

Hillary Vaughn Age: A Generational Bridge in Public Service and Policy

<i>XXVI</i>

A Glimpse Into Jim Parsons’ Personal World: How the Icon Behind ‘spoiler Lert’ Brings Authenticity to His Craft

