IMT Ibu: The Complete Guide to Transforming Digital Supply Chains with Intelligent Automation
IMT Ibu: The Complete Guide to Transforming Digital Supply Chains with Intelligent Automation
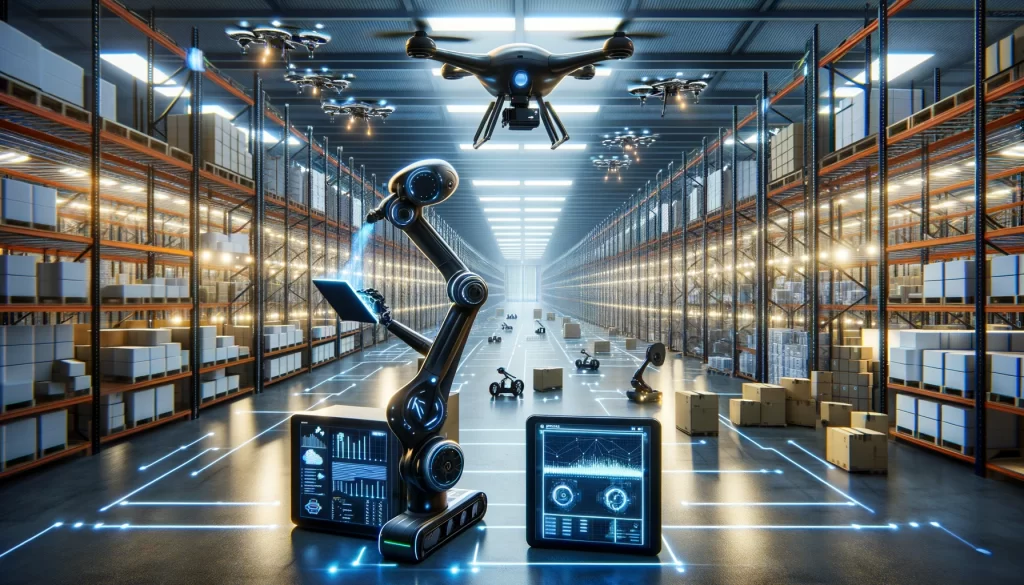
In an era defined by supply chain volatility and relentless demand for speed and precision, IMT Ibu emerges as a pioneering framework that integrates intelligent automation into core logistics and operational workflows. This comprehensive guide unpacks IMT Ibu’s foundational principles, practical applications, and strategic impact across industries—proving it’s more than a technological upgrade, but a complete operational revolution. From AI-driven forecasting and robotic process automation to blockchain-enabled transparency, the IMT Ibu model delivers measurable efficiency, risk mitigation, and scalability.
As businesses confront the complexities of global trade and digital transformation, understanding IMT Ibu’s structure, implementation, and outcomes becomes essential for leaders seeking sustainable competitive advantage.
The Core Architecture of IMT Ibu: Intelligent Automation in Supply Chain Science
At its essence, IMT Ibu represents a systematic integration of artificial intelligence, data analytics, and automation technologies into the supply chain ecosystem. It goes beyond siloed system upgrades, offering a holistic operational framework that aligns technology with human expertise. The model is built on four interdependent pillars:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging real-time analytics and predictive modeling to transform raw data into actionable insights.
- Autonomous Process Automation: Deploying robotic process automation (RPA) and intelligent workflows to eliminate manual bottlenecks.
- Digital Twin Simulation: Creating virtual replicas of physical supply chains to test scenarios, optimize inventory, and preempt disruptions.
- Blockchain-Powered Traceability: Ensuring end-to-end visibility and trust through immutable transaction records across suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
“IMT Ibu is not just automation,” explains Dr.
Lina Chen, a logistics technology analyst at supplychainconstellations.org. “It’s a cognitive infrastructure that learns, adapts, and responds—turning static chains into dynamic, self-optimizing networks.”
From Theory to Practice: Real-World Applications of IMT Ibu Across Industries
The true power of IMT Ibu lies in its adaptability. Across manufacturing, retail, logistics, and healthcare, organizations have leveraged the framework to achieve breakthrough results.
Key use cases include:
- Demand Forecasting Enhancement: By applying machine learning algorithms to historical sales, market trends, and external variables (weather, events), companies reduce forecast errors by up to 40%, minimizing overstock and out-of-stocks.
- Warehouse and Fulfillment Optimization: Autonomous robots and smart routing systems, guided by IMT Ibu’s automation layers, cut order processing time by 50% and increase warehouse throughput.
- Supplier Risk Management: Blockchain integration enables real-time verification of supplier compliance, quality, and delivery timelines, slashing supply chain uncertainty.
- Last-Mile Delivery Innovation: AI-powered route optimization and drone delivery coordination within the IMT Ibu ecosystem improve delivery accuracy and reduce carbon emissions.
In one documented case, a multinational automotive parts distributor implemented IMT Ibu’s automation suite and achieved a 38% reduction in logistics costs within 18 months, while improving on-time delivery rates from 82% to 97%.
Implementing IMT Ibu: A Phased Approach for Organizational Success
Rolling out IMT Ibu is not a one-time tech fix but a strategic transformation requiring careful planning, leadership alignment, and cultural adaptation. Experts recommend a phased deployment model:
- Assessment & Goal Setting: Audit existing supply chain processes, pinpoint bottlenecks, and define clear KPIs—such as lead time reduction or inventory turnover improvement—aligned with business objectives.
- Pilot Testing: Select a segment—like a regional distribution hub—and deploy targeted automation tools to validate impact, gather feedback, and refine workflows.
- Scalable Integration: Expand successful pilots using modular technology stacks, ensuring interoperability between legacy systems and new IMT Ibu platforms.
- Change Management: Invest in training, upskilling, and stakeholder engagement to foster adoption and harness human-technology collaboration.
“Organizations that treat IMT Ibu as a triple-loop transformation—technology, process, and culture—derive the highest value,” notes Raj Patel, a senior consultant at supplychaininnovations llc. “It’s not about replacing people, but empowering them with smarter tools.”
Measuring Impact: Key Metrics and ROI of IMT Ibu Adoption
Quantifying the return on investment (ROI) is critical to validating IMT Ibu’s strategic value.
Tracking specific performance indicators reveals clear benefits:
- Operational Efficiency: Measured by reduced cycle times, lower error rates, and higher throughput—often with improvements exceeding 30% within first-year deployments.
- Cost Savings: Decreases in labor, inventory holding costs, and logistics inefficiencies contribute to positive net margin expansion.
- Risk Mitigation: Enhanced visibility reduces exposure to disruptions, with fewer stockouts and faster response to geopolitical or natural crises.
- Customer Satisfaction: Consistent delivery performance strengthens trust and repeat business, directly influencing revenue growth.
For example, a global consumer goods firm reported a 22% drop in supply chain incidents and a 19% increase in net profit margin after full IMT Ibu integration—metrics that underscore its financial and strategic strength.
Challenges, Pitfalls, and How to Navigate Them
Despite its advantages, adopting IMT Ibu is not without hurdles. Common challenges include:
- Legacy System Integration: Older IT infrastructures often resist seamless connectivity; APIs and middleware solutions are critical to bridge gaps.
- Data Quality and Governance: Automation relies on accurate, clean data—poor data hygiene undermines AI accuracy and decision quality.
- Change Resistance: Employees and managers may fear disruption; transparent communication and inclusive design reduce friction.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Expanded digital footprints increase vulnerability—proactive measures like encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring are essential.
“The most successful implementations treat these challenges as innovation opportunities,” advises Dr. Chen.
“Testing, iterating, and empowering cross-functional teams builds resilience and long-term adoption.”
The IMT Ibu framework represents a paradigm shift in how businesses architect their supply chains—moving from reactive, fragmented systems to proactive, intelligent networks. By weaving together data, automation, and transparency, it delivers not only operational excellence but strategic resilience in an era of constant change. As global markets grow more interconnected and unpredictable, adopting IMT Ibu isn’t optional—it’s the blueprint for future-ready supply chains.
For forward-thinking organizations, the path forward is clear: embrace intelligent automation, and transform disruption into opportunity.



Related Post
Pictures From Hisashi Ouchi Hospital: An Inside Look At A Tragic Medical Adventure

Emmanuel Acho Married: Behind the Public Persona, The Real Story of the Former NFL Player’s Committed Union

Soekarno Hatta Airport Traffic Today: What You Need To Know

Unraveling Jaclyn Elmquist Autopsy: Groundbreaking Findings That Redefined a Tragedy

