How to Make Pistons: The Expert Guide to Precision and Performance
How to Make Pistons: The Expert Guide to Precision and Performance
From high-performance engines in sports cars to robust industrial machinery, pistons form the mechanical heartbeat of power transfer—converting pressure into motion with precision and strength. Constructing effective pistons demands a fusion of metallurgical insight, engineering rigor, and hands-on craftsmanship. This comprehensive guide reveals how to design and fabricate pistons that deliver durability, efficiency, and reliability under extreme conditions, whether for racing or manufacturing.
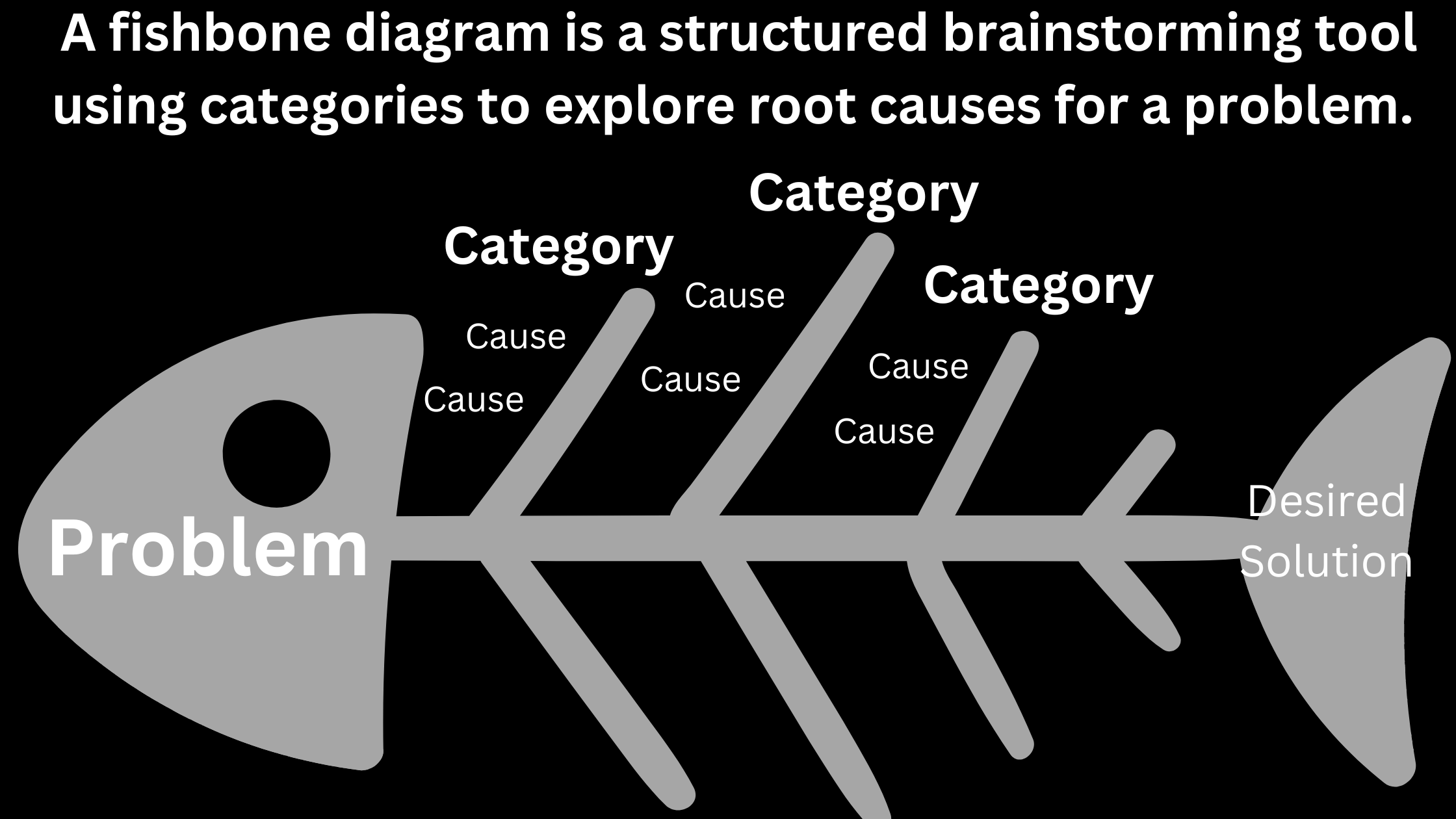
Understanding the Core Components of Piston Design
Pistons are not merely cylindrical parts; they are engineered systems integrating several critical elements.At their core, pistons must withstand high thermal loads, intense mechanical stress, and repeated compression cycles. Key components include the piston crown, shelf, skirts, and land sections—each tailored to manage forces, minimize wear, and optimize sealing. The **piston crown** determines combustion chamber geometry and heat distribution, directly impacting efficiency and emissions.
The **skirt** reduces friction and absorbs lateral forces during movement. Meanwhile, **land depth and profile** influence gas sealing and thermal expansion. “A piston’s success begins with perfect alignment of form and function,” explains engine design specialist Dr.
Lena Torres. “Every dimension must serve a clear purpose—from stroke length to material response.”
Materials selection follows design priorities. Common alloys include aluminum-silicon for lightweight durability, cast iron for heavy-duty reliability, and advanced composites in racing applications where weight savings outweigh cost.
The choice hinges on operating environment, load, and performance targets.
Step-by-Step: From Planning to Fabrication
Creating pistons begins long before machining—planning sets the foundation. The process unfolds in key stages that blend digital simulation with physical manufacturing precision.Finite element analysis (FEA) simulates thermal, torsional, and fatigue stresses across operating cycles, pinpointing weak points before production. Critical parameters include compression ratio compatibility, clearance referencing, and surface finishes. “Simulation lets you predict failure points down to the micron—preventing costly faults post-prototype,” notes automotive metallurgist Marcus Hale.
Multi-axis CNC machining then mills crowns, lands, and skirts to tight tolerances—often to within 0.002 inches—ensuring proper gas sealing and minimizing friction. Surface refinement via grinding or polishing prevents micro-fractures and prolongs fatigue life.
This step is pivotal; improper treatment can trigger premature cracking or reduced fatigue strength. “Even a minor deviation in heat duration or temperature compromises piston integrity,” warns quality control expert Elena Cho.
Every piston undergoes rigorous non-destructive testing: dye penetrant inspection, ultrasonic scanning, and dynamic clearance checks ensure conformance to specifications.
Each phase integrates science and craftsmanship, transforming raw material into a precision component engineered to endure millions of strokes.
Material Selection: Matching Alloys to Function
Choosing the right material defines a piston’s performance envelope. Aluminum-silicon alloys dominate in engines requiring low weight without sacrificing strength, making them standard for performance and consumer vehicles.Their lightweight nature improves fuel efficiency and acceleration response, particularly vital in racing applications. Cast iron, by contrast, excels in heavy-duty applications—such as industrial compressors or compressor




Related Post
Devon Aoki’s Cinegraphic Legacy: The Essential Films and Defining Roles That Defined Her Stardom

Unveiling the Dynamic Duo: Kat On Gutfeld Husband

Kristin Kreuk Married: Unveiling the Truth Behind the Rumors That Swirled for Years
The Square Root of 100: A Deeper Dive into an Everywhere Constant

