39 International Code: The Shifting Foundation of Global Legal Compliance
39 International Code: The Shifting Foundation of Global Legal Compliance
In an age where digital operations span continents and supply chains thread through multiple jurisdictions, the 39 International Code stands as a cornerstone framework shaping how governments, businesses, and communities align with international legal standards. This foundational Code—encompassing human rights, cross-border trade, data protection, and environmental stewardship—does more than codify rules: it harmonizes disparate legal systems into a coherent, enforceable structure that underpins global order. As global mobility and interconnectedness intensify, understanding the depth, reach, and real-world applications of the 39 International Code is essential for anyone navigating modern legality.
The 39 International Code emerged from decades of multilateral negotiations, crystallizing multitudes of treaties, protocols, and soft law instruments into a single, authoritative compilation. Originally conceived to unify fragmented legal approaches post-WWII, it now serves as a dynamic reference point for state compliance and corporate accountability. Its core mission: to balance national sovereignty with universal principles, enabling cooperation without eroding local legal identities.
Each of the 39 core provisions addresses a distinct yet interwoven domain. For instance, Article 3 (Fundamental Rights) asserts inescapable principles—life, liberty, and physical integrity—while Article 12 (Data Privacy) mandates cross-border data transfer safeguards critical to the digital economy. Article 24 (Sustainable Development) compels signatories to integrate environmental protection into policy-making, reflecting a global consensus on ecological limits.
Key Pillars of the 39 International Code: • Human dignity and non-discrimination—enshrined across nearly every article, reaffirming universal values. • Economic enfranchisement, particularly through fair trade and labor standards, ensuring equitable participation. • Cybersecurity and information governance, governing how digital footprints cross borders.
• Climate accountability, embedding emissions reduction and adaptation mandates. • Transparency and due process in dispute resolution, bridging legal systems with enforceable certainty. Rather than a static list, the Code functions as a living framework, evolving through amendatory protocols ratified by 160+ nations.
“The 39 International Code is not just a document—it’s a contract between nations and peoples,” states legal analyst Dr. Elena Markov of International Law Review. “It acknowledges diversity but demands shared standards.”
Geografieistically, the Code’s influence is truly planetary.
African signatories such as Kenya and South Africa leverage Articles 7 (People’s Rights) and 15 (Freedom of Informed Consent) to strengthen anti-corruption and digital governance. In Asia, Indonesia and Vietnam align manufacturing and export policies with Articles 20 (Environmental Protection) and 31 (Worker Safety). European states reinforce enforcement via domestic courts citing Article 5 on supranational oversight.
The Americas see unique adaptation—Mexico’s trade ministries cite Article 44 on fair competition, while Brazil’s environmental agencies invoke Article 27 on forest preservation.
In practice, the Code drives compliance through multiple channels. Multinational enterprises embed its principles into supply chain audits, ensuring customs, labor, and environmental checks meet international benchmarks.
Governments establish domestic authorities—like India’s Data Protection Board—to interpret and enforce Article 12 rigorously. Courts reference specific provisions to resolve disputes; in 2023, a landmark case in Costa Rica applied Article 21 (Right to a Healthy Environment) to block a mining project violating watershed protections.
Critics argue enforcement remains uneven, dependent on political will and resource capacity.
Yet, the Code’s value lies in its normative power: it sets measurable expectations, dwells in public consciousness, and enables civil society to hold authorities and corporations to account. “Compliance isn’t just legal—it’s reputational,” notes Lucian Hartmann, policy lead at Global Compliance Forum. “Companies that align with the Code often gain competitive advantage through trust and market access.”
Looking forward, emerging challenges—artificial intelligence ethics, climate migration, and quantum computing—demand proactive adaptation.
Expert panels are already drafting supplements to Article 18 (Technological Innovation) and Article 32 (Climate Adaptation). “The 39 International Code must breathe with reality,” asserts Dr. Maria Chen, UN Special Rapporteur on Global Legal Integration.
“Its strength lies in its ability to evolve while preserving core humanity.”
From trade treaties to public health, the 39 International Code forms an intricate lattice safeguarding humanity’s collective future. It is at once a legal compass, a diplomatic achievement, and a call to shared responsibility—enforcing not just rules, but respect across borders. As globalization deepens, this Code remains the invisible hand steering the world toward coherence, justice, and sustainability.
In essence, the 39 International Code is the living contract binding nations and people in a shared pursuit of order and equity. Its provisions are not ideals confined to paper—they shape markets, influence policy, and empower individuals. In a fractured world, it stands as a testament to what global cooperation can achieve.
The Code endures not by accident, but by necessity—a beacon of what international law can and must become.




Related Post
Unlock Yellowstone’s Wild Secrets:master the Yellowstone Lower Loop Map for Epic Road Adventures

Skip the Line: Decadent Blueberry Muffin & Strawberry Shortcake Recipes That Deliver Every Bite
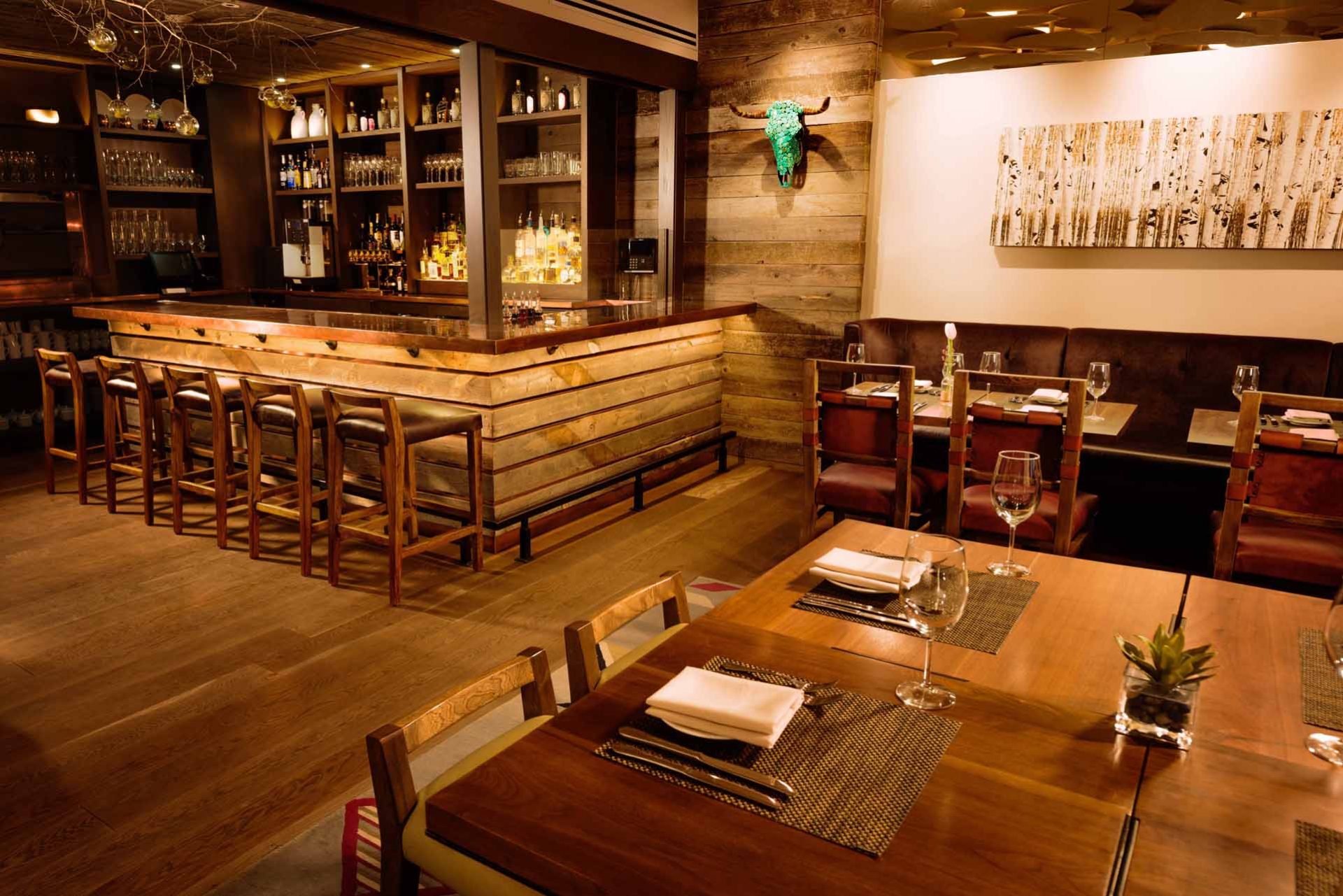

Figs Jackson Hole: Where Desert Charm Meets Mountain Luxury

Hillary Vaughn Age: A Generational Bridge in Public Service and Policy

