1 Mile to Meters: The Essential Conversion That Shapes Global Understanding
1 Mile to Meters: The Essential Conversion That Shapes Global Understanding
Converting 1 mile to meters is more than a mere unit switch—it’s a gateway to understanding how global systems standardize distance measurement. At its core, this conversion bridges two dominant systems: the United States’ imperial mile and the international metric mile. While the mile remains deeply embedded in American culture and infrastructure, the meter serves as the universal benchmark across science, navigation, and everyday international communication.
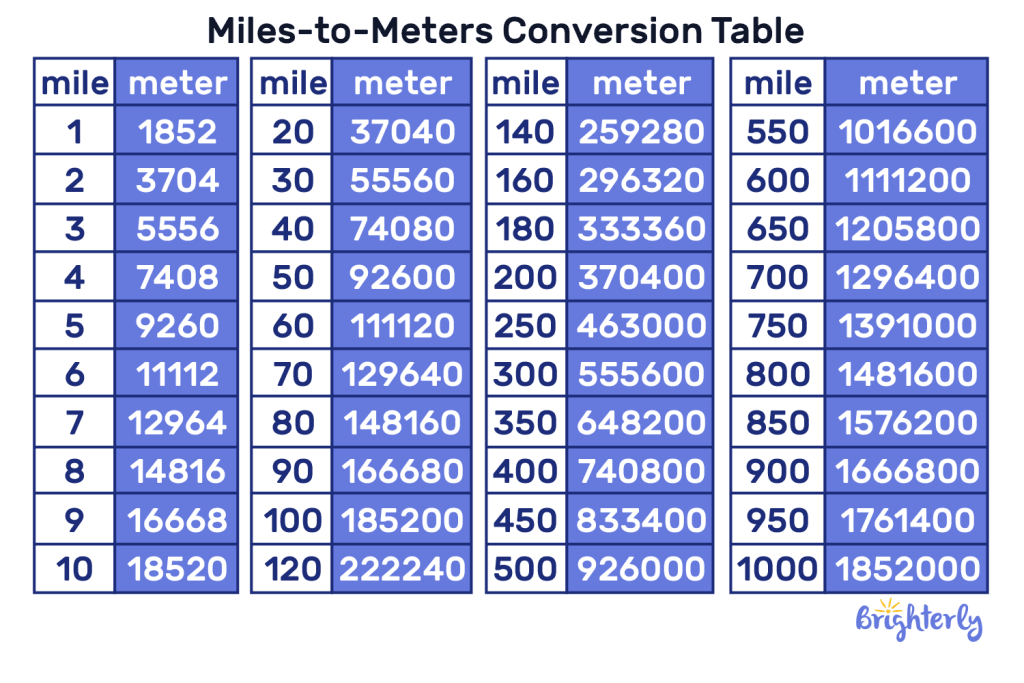
The precise figure—1 mile equals exactly 1,609.344 meters—carries weight far beyond a simple number, influencing everything from road signage to satellite navigation. Understanding this conversion hinges on the historical and scientific foundations behind both units. The modern international mile traces its roots to the English statute mile, formally standardized in 1959 as part of the metric system’s expansion.
Originally defined by ancient Roman standards—where a mile meant “a thousand paces,” roughly 5,280 feet—the modern mile was recalibrated using metric principles. This redefinition ensured consistency across borders, fostering trade, travel, and data exchange. In contrast, the U.S.
mile evolved from colonial-era foot-based measurements, retaining its imperial identity with no formal redefinition.
To convert miles to meters with absolute clarity, the transformation formula uses a fixed conversion factor: 1 mile = 1,609.344 meters. This precise decimal value reflects the relationship established during the 1959 agreement between British and U.S.
representatives, who standardized metric units for mutual compatibility. Applying this, 1 mile exactly equals 1,609.344 meters—a figure that emerges not from arbitrary rounding, but from intentional international alignment. Every step of this calculation reinforces the reliability of cross-cultural measurement systems.
Quantifying the Conversion: 1 Mile in Meters
- 1 mile = 1,609.344 meters (exact) - This equivalence is constant, regardless of region or application - No regional variations alter the fundamental ratioThe practical implications of this conversion are vast and varied. In transportation, for example, road signs in the U.S. use miles, while global systems like GPS, aviation navigation, and shipping logs rely on meters.
A driver traveling from New York to London must mentally—or mathematically—shift from miles to meters to align with international route-planning tools. Within urban planning, airport runways, cycling paths, and wilderness trails depend on accurate, standardized measurements—meters ensuring uniformity across borders. Even in emerging fields like drone navigation and autonomous vehicle systems, precise conversion remains essential to avoid errors that could compromise safety or efficiency.
From Miles to Meters: Global Standards and Real-World Use
The cooperation between metric and imperial systems reflects a broader trend: the gradual integration of metric standards into societies most resistant to change.Even in the U.S., where miles dominate public life, engineers, scientists, and software developers routinely convert miles to meters for compatibility with global databases, construction blueprints, and environmental monitoring tools. The International System of Units (SI) mandates meter precision, but practical adoption varies. In contrast, countries fully transitioned to metric systems—such as those in the European Union—use meters by default, minimizing confusion in international projects like railway interoperability or climate research networks.
Historical Context and Continental Variance
The divergence between mile and meter usage underscores a century-long evolution in


Related Post

What Is Joey Jones Salary on Fox: Inside the Public-est Kevin’s Compensation

Everything You Need To Know About Vegamovies: The Ultimate Guide to India’s Leading Movie Download Platform

Denilson Pereira Neves: The Untold Story on Instagram That Defies Expectation

Understanding Tan Chuan Jin’s Divorce: Legal Nuance, Social Ripple Effects, and What It Reveals About Modern Marriage

